Well logging
Formation testing
Drill stem testing (DST)
Open-hole formation testing during drilling is performed after penetrating promising intervals. Maximum possible preservation of natural porosity and permeability of drilled rocks and ensuring hydraulic communication between rocks and well are the prerequisites for obtaining reliable data. This is achieved by controlling physical and chemical parameters of drilling mud used for penetrating target formations.
Cased-hole formation testing is performed for testing (stimulating) low-producing perforated formations, draining (cleaning) of bottomhole, detecting leakages of cement plugs and casing string.
Testing is performed using multi-cycle drill pipe or tubing conveyed tool. Valve system of the tester is operated by rotation and vertical travel of the drill (tubing) string. Testing includes formation fluid sampling, continuous recording of pressure and temperature above and below packer using self-contained digital pressure gauges (DPG). After testing and pulling out equipment, DPG data is used to calculate hydrodynamic parameters of formation and evaluate quality of performed testing.
Main advantages of this technology:
- Direct evaluation of reservoir saturation type;
- Possibility of selective testing of formations using two-packer system;
- Small volume of space below packer allows to reduce testing time, as well as to obtain accurate data on hydrodynamic parameters of formation, including skin factor.
Available test systems:
- KII-95 is intended for cased-hole testing in wells of size from 127 to 178 mm and for open-hole testing in wells of size from 118 to 161 mm;
- KII-146 is intended for open-hole testing in wells of size from 187 to 295 mm and for cased-hole testing in wells of size from 219 to 324 mm.
Wireline formation testing
Wireline formation testing is performed using AGIP-K tool. Testing is aimed at determining saturation types of reservoirs and evaluating their hydrodynamic parameters. There are two testing modes:
- Production logging;
- Formation testing.
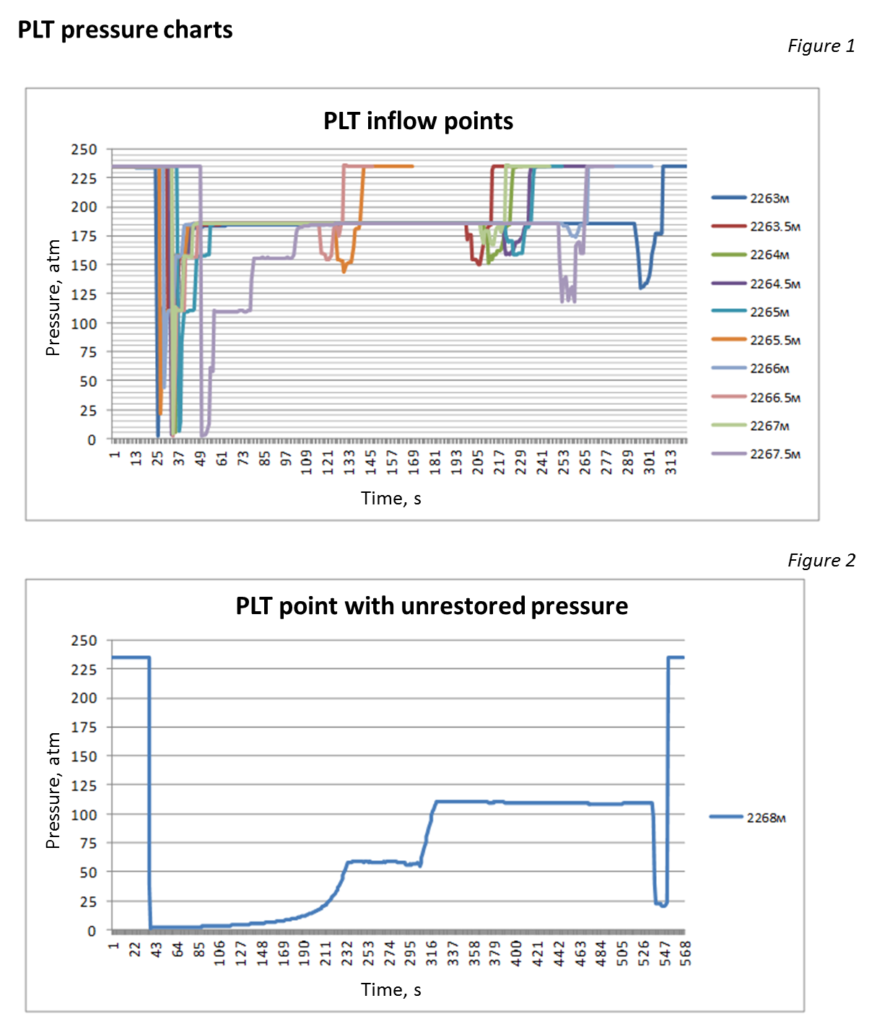
Production logging mode assumes multiple stimulation tests from target formations or intervals of one formation during one tool trip in order to:
- Identify reservoirs;
- Evaluate net thickness of reservoirs;
- Build reservoir pressure profile;
- Evaluate productivity and permeability of reservoirs;
- Select the most permeable intervals of formation for formation fluid sampling.
Formation testing mode assumes taking one downhole fluid sample from target formation or formation interval during one tool trip in order to:
- Evaluate reservoir saturation type;
- Further use of sample for component analysis.
Technology advantages:
- Evaluation of hydrodynamic parameters of various formation intervals during one round trip in the production logging mode;
- Defining formation pressure profile;
- Identification of abnormally high and low formation pressure zones in exploration wells;
- Identification of depleted low-pressure zones, water breakthrough zones from injection wells in new production wells;
- Evaluation of possibility of inflow from reservoir;
- Evaluation of fluid contact and transition zone depths;
- No risk of flowing during testing.
AGIP-K application conditions and specifications:
- Maximum temperature: 120 deg. C;
- Maximum pressure: 60 MPa;
- Minimum operation pressure: 8 MPa;
- Tool diameter: 132 mm;
- Number of test points in production logging mode during 1 round-trip: from 10 to 60 (depending in permeability);
- Sample volume in formation testing mode: 7 (14) L;
- Maximum well deviation angle: 30 deg.